11 Severe Side Effects of Almond Milk You Should Know
Almond milk gets mentioned as one of the most celebrated plant-based milk. But it may not be as nutritious. Know the side effects of almond milk you may have missed.
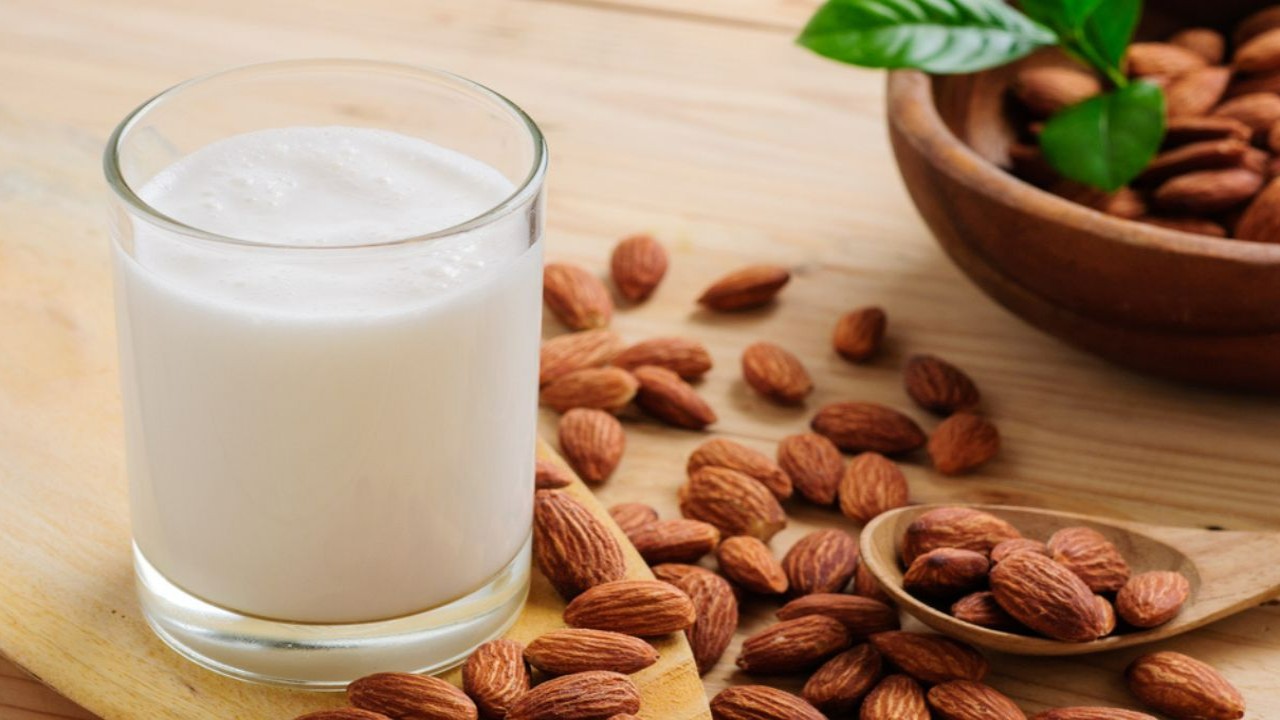

Finding healthier drinking options is a good way to prevent yourself from binge eating. However, it’s important to find the nutritional value of what you consume. The side effects of almond milk may surprise you, but not pleasantly. Almond milk might be a good alternative for lactose intolerant individuals but as Valerie Agyemen, a renowned Dietician Nutrition says, “Almond milk is nutritious but it isn’t as nutritious as cow’s milk.” So, you may want to check whether the nutritional value your body needs or what you expect of almond milk is met or not. Let’s delve deeper to find out more about almond milk, and whether almond milk is good for you.
What Is Almond Milk?
Almonds are vital sources of many nutrients including proteins, fiber, vitamin E, and manganese (1). They also contain high amounts of monounsaturated fatty acids that may contribute to weight loss and weight management (1). Owing to their immense nutritional value, they are used to prepare almond milk which is a colloidal mixture obtained after mixing water with powdered or pasted almonds (1). The general preparation method for making almond milk includes (1):
- Soaking almonds in water overnight
- Blanching/ removing almond kernels or skins
- Grinding almonds to a finer paste while adding water
- Filtering the solid solution properly
- The thicker, milkier liquid that remains is the almond milk
- You may add more water to it for making it thicker
- In commercial industries, additionally, this liquid is homogenized under high pressure followed by pasteurization to enhance its shelf life.
- Sweeteners or artificial flavors may also be added to it.
- Sometimes thickening agents like carrageenan may also be added for a smoother texture of the almond milk.
Now, your question might be, is almond milk healthy?
Almond milk doesn’t contain much protein or nutrient density but has a good calcium content and a nutty flavor to it that might make its consumption pleasant (1). Compared to soy, goat’s, and cow’s milk, almond milk provides less than half of the proteins they provide (2).
11 Side Effects of Almond Milk
Almond milk might be your alternative lactose-free drink, but you may need to familiarize yourself with the side effects of almond milk too, like (3),(4):
- Allergies: If you have nut allergies, you might feel allergic to almond milk. According to a survey, almost 3% of the global population is affected by food allergies (5). Almonds are among the most widely consumed tree nuts (6). However, tree nuts are proven to be responsible for the most acute and fatal allergies including oral allergy syndrome reactions (7). And, unfortunately, tree nut allergies don’t have a lot of effective treatments (8).
- Digestive Issues: Excessive consumption of almond milk may trigger various digestive issues like stomach discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea. There is also evidence that suggests intake of finely ground almonds is better and digested almonds may cause swelling in the gut (9).
- Reduces Nutrient Absorption: Almond milk may block the absorption of zinc, iron, and magnesium because of the percentage of phytic acid in it. The presence of phytic acid in the gastrointestinal tract has proven to result in poor bioavailability or absorption of these minerals (10).
- Goitrogenic Nature: If you’re suffering from impaired thyroid function, you may stop consuming almond milk or limit its consumption. Unpasteurized almond milk has also been tested to contain a potentially lethal percentage of total cyanide that is toxic to health (11). Cyanide has also been recognized as a rapidly acting substance or poisonous (12).
- Constitutes Carrageenan: There might be a certain percentage of carrageenan in almond milk which is harmful to the gastrointestinal tract. Both degraded as well as undegraded Carrageenan has proven to contribute to intestinal ulcers and neoplasms (4). Our contributor Kelsey Costa, MS, RDN and nutrition research specialist, explains that, “Carrageenan, a common food additive derived from red seaweed, is generally recognized as safe by the FDA. However, some research suggests it may cause inflammation and damage in the gastrointestinal tract. Still, more studies are needed to understand the potential health impacts fully.”
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Almond milk is not suitable for children under the age of 1 year as it might not be able to meet their nutritional requirements. As such, it may not be considered a substitute for cow’s milk as its inappropriate substitution may contribute to nutritional deficiencies (13). Apart from that, you may take it only at room temperature as boiling reduces its nutritional value.
- Artificial Sweetening Requirements: Since almond milk is not naturally sweet, it may either require additional sweetening or some brands may add artificial sweetening agents to it. Consuming artificial sweeteners has no positive impact on health but may cause weight gain (14). Sweetened vanilla-flavored almond milk contains almost 16 grams of sugar. And, it might also be overwhelming to keep a close eye on all the brands and labels that don’t offer sweetened variations of almond milk. So, if at all you want to consume it on a daily basis, have unsweetened almond milk instead and try preparing it at home naturally.
- Inadequate Iodine Content: There has been evidence indicating that individuals who consume almond milk may be at risk of inadequate iodine intake (15). So, when you are substituting almond milk for cow’s milk, you may look for other options to fulfill your iodine requirements.
- Metabolic Disturbances: A recent study indicates that consuming plant-based drinks may cause metabolic disturbances in children and adults as well (16). There has also been evidence that almond milk doesn’t fulfill many nutritional requirements and may be avoided to maintain good metabolism. To be precise, if you’re not having almond milk, you are not losing on much and might as well fulfill your dietary requirements with better options.
- Disturbs Protein Retention: AAlmond milk is quickly aggregated, creamed, and layered in the stomach and may induce a faster gastric emptying of proteins (17). However, as our contributor Kelsey Costa adds, “Almond milk contains less protein than cow’s milk, but while it’s not a direct high protein source, it doesn’t cause protein depletion in the body either.”
- Erosive Potential: Almond milk has a higher buffering capacity and that might be associated with more erosive potential for teeth (17) Cow’s milk is good for teeth so having almond milk instead of that may cause dental erosion, and might as well not provide the nutrients needed by teeth (18).
- Digestive Issues: Excessive consumption of almond milk may trigger various digestive issues like stomach discomfort, nausea, and diarrhea. There is also evidence that suggests intake of finely ground almonds is better and digested almonds may cause swelling in the gut (9).
- Reduces Nutrient Absorption: Almond milk may block the absorption of zinc, iron, and magnesium because of the percentage of phytic acid in it. The presence of phytic acid in the gastrointestinal tract has proven to result in poor bioavailability or absorption of these minerals (19). So, while you’re not getting a lot of nutrients from consuming it, you risk the absorption of other vital elements.
Conclusion
While we may love finding alternatives to dairy products, especially milk, we may overlook the lack of nutrition and prominence of harmful agents in substitute plant-based milk and drinks. The side effects of almond milk should be taken seriously. For infants as well as adults, almond milk may do more bad than good. It’s important to check the labels of the almond milk brands as well as the nutritional expectations you may have from them.
Contributor: Kelsey Costa, MS, RDN, and Owner of Nutrition Insights LLC





 JOIN OUR WHATSAPP CHANNEL
JOIN OUR WHATSAPP CHANNEL