Ganglion Cyst Home Treatment – Get Rid of It Using These Natural Remedies
Have a suspicious fluid-filled lump on your finger? It could be a ganglion cyst! Find out what it is, its causes and treatment options, both at-home and medical!
Welcome to the annoying world of ganglion cysts, enigmatic companions that often take up residence in wrists, hands, and other joints. These benign but perplexing growths, though harmless, can challenge our mobility and aesthetic sensibilities. Let’s take a look at the intricacies of ganglion cysts, explore their origins, and discover how to get rid of them for good. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for ganglion cysts.
What Is a Ganglion Cyst?
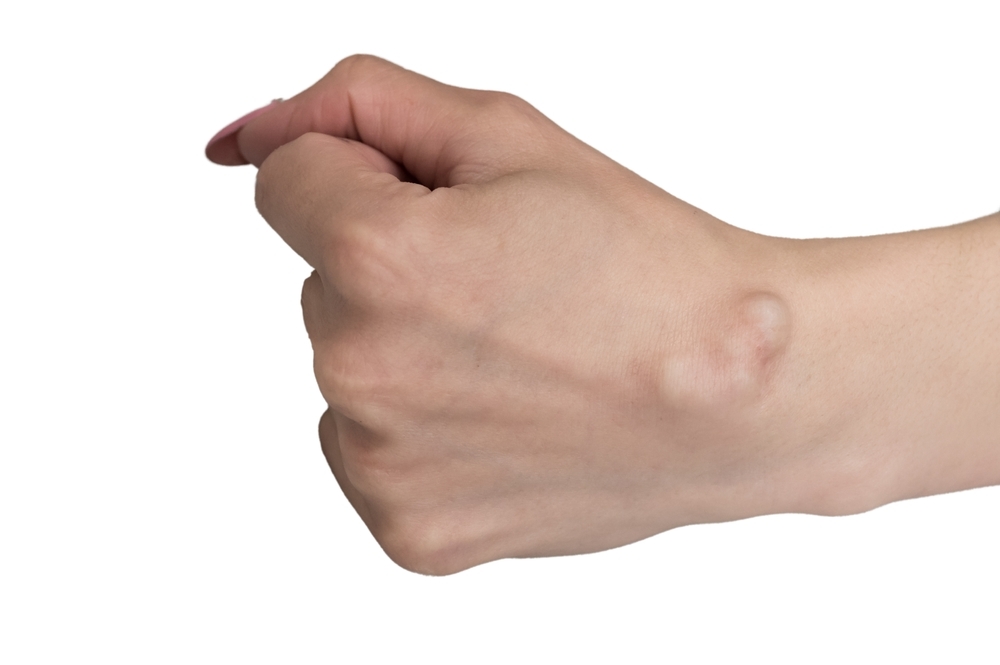
A ganglion cyst is a common noncancerous lump that typically appears as a gooey fluid-filled sac near tendons or joints, most commonly found in the wrist or hand (1). These cysts can also occur in other areas of the body, such as the ankle or foot. Ganglion cysts are often round or oval-shaped and can range in size from a small pea to a larger marble.
The fluid within a ganglion cyst is known as synovial fluid, which is the lubricating fluid found in joints and tendons. It helps reduce friction and allows smooth movement of the joints. Ganglion cysts form when there is a leakage or bulging of this fluid, leading to the formation of a sac or cyst.
The exact cause of ganglion cysts is not fully understood, but they are believed to be related to joint or tendon irritation or trauma. It is thought that repetitive stress or injury to a joint or tendon may cause the joint lining or tendon sheath to bulge, forming a cyst. However, in many cases, the exact trigger remains unknown.
Ganglion cysts are generally benign and do not spread to other parts of the body or become cancerous. They are most commonly found in women between the ages of 20 and 40, but they can occur in individuals of any age or gender.
While ganglion cysts are usually painless, they can cause discomfort if they press on nearby nerves. In some cases, the cysts may interfere with joint movement or cause cosmetic concerns due to their appearance. Ganglion cyst treatments include observation, aspiration (fluid removal), and surgical removal, depending on the location, size, and symptoms of the cyst.
Ganglion Cyst Home Treatment Options
1. Lemongrass Essential Oil

Due to its pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties, lemongrass oil has the potential to assist in pain reduction and the drainage of fluid from the cyst (2).
You Will Need
- 2 drops of lemongrass oil
- 1/2 teaspoon of coconut oil
What You Have To Do
- Add the lemongrass oil to the coconut oil.
- Mix well and apply this mixture to the affected joint.
- Leave it on for at least twenty minutes before washing it off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 3-4 times daily.
2. Epsom Salt Soak
The immunomodulatory properties of magnesium in Epsom salt contribute to a reduction in the production of inflammatory cytokines within the body (3). This, in turn, aids in alleviating pain, inflammation, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
You Will Need
- ½ cup of Epsom salt
- A basin of warm water
What You Have To Do
- Add the Epsom salt to a basin of warm water.
- Soak the affected area in this for twenty minutes.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this once daily or every alternate day.
3. Frankincense Essential Oil
With its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, frankincense oil exhibits the potential to offer pain relief and expedite the healing process of the cyst (4).
You Will Need
- 2-3 drops of pure frankincense oil
What You Have To Do
- Apply two to three drops of frankincense oil directly to the affected joint.
- Leave it on.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 2 times daily.
4. Tea Tree Oil

Tea tree oil, known for its anti-inflammatory properties, has the potential to assist in reducing inflammation and preventing fluid accumulation within the cyst (5).
You Will Need
- 3 drops of tea tree oil
- 1 teaspoon of coconut oil
- Band-Aid
What You Have To Do
- Mix the tea tree oil with the coconut oil.
- Apply it to the affected area.
- Cover the cyst with a Band-Aid and leave it on.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this once daily.
5. Tea Bag
Tea, known for its anti-inflammatory and healing properties, can potentially aid in the healing process of a ganglion cyst and provide relief from associated pain (6).
You Will Need
- Used black or herbal tea bags
What You Have To Do
- Place a used black tea bag on the affected joint.
- Leave it on for thirty minutes.
- Wash the area with water.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 2-3 times daily.
6. Castor Oil

Due to the presence of ricinoleic acid, which possesses anti-inflammatory properties, castor oil can be considered a potential treatment option for addressing inflammation and reducing swelling in the affected area (7).
You Will Need
- 100% organic castor oil
What You Have To Do
- Apply castor oil to the affected joint.
- Cover the area with a bandage.
- Leave it on for about twenty minutes.
- Wash it off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 1-2 times daily.
7. K Tape
By providing support and stability to the affected joint, K tape can assist in the healing process of a ganglion cyst (8). Additionally, it has the potential to alleviate pain and enhance muscle strength, further contributing to overall recovery.
You Will Need
- A K tape
What You Have To Do
- Bend the affected joint of your wrist or foot.
- Stick the K tape along the affected area without stretching your joint.
- Wear it for a couple of days.
How Often You Should Do This
You must keep this tape on the affected joint for 2-3 days.
8. Warm Compress
The application of a warm compress is considered an effective therapy for ganglion cysts as it serves a dual purpose. It can provide relief from inflammation, while also soothing the associated pain (9).
You Will Need
- A warm compress
What You Have To Do
- Place a warm compress or a hot water bottle on the affected area.
- Leave it on for about 5 to 10 minutes and remove.
- Repeat 2 to 3 times.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this whenever you want quick relief.
9. Aloe Vera

Aloe vera, renowned for its natural healing properties, can be beneficial in the treatment of ganglion cysts. In addition, it may aid in reducing swelling and inflammation in the affected area (10).
You Will Need
- Freshly extracted aloe gel
What You Have To Do
- Apply the gel directly to the affected area.
- Leave it on for at least thirty minutes.
- Rinse it off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 2-3 times daily.
10. Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar, rich in acetic acid, possesses anti-inflammatory properties that may aid in reducing inflammation, swelling, and pain associated with ganglion cysts (11). It can potentially serve as a natural remedy for managing the symptoms of the condition.
You Will Need
- 1 tsp of organic apple cider vinegar
- 250ml of water
- Cotton balls
What You Have To Do
- Add the apple cider vinegar to the water.
- Soak a cotton ball in this solution and place it on the cyst.
- Leave it on for at least 30 minutes before washing it off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 2-3 times daily.
11. Turmeric

Turmeric, specifically its active compound curcumin, is known for its anti-inflammatory properties (12). Utilizing turmeric may help in combating inflammation, reducing swelling, and alleviating pain associated with ganglion cysts.
You Will Need
- 1 teaspoon of turmeric powder
- Water (as required)
What You Have To Do
- Add a few drops of water to a teaspoon of turmeric powder to make a thick paste.
- Apply this directly to the affected area.
- Leave it on for 30 minutes and rinse off.
How Often You Should Do This
Do this 1-2 times daily.
12. Vitamin B-Complex
Vitamin B-complex, a group of water-soluble vitamins essential for cell metabolism, can potentially aid in the healing process of ganglion cysts (13). Consuming foods rich in vitamin B-complex, such as berries, lean meat, eggs, legumes, tuna, avocado, and spinach, can be beneficial. Alternatively, after consulting with a healthcare professional, you may consider taking vitamin B-complex supplements to ensure adequate intake.
Ganglion Cyst Medical Treatments

Medical ganglion cyst treatments may vary depending on the size, location, symptoms, and individual preferences. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Observation/Watchful Waiting:
If the ganglion cyst is small, painless, and does not cause any functional limitations or discomfort, a doctor may recommend simply monitoring the cyst over time without intervention. Ganglion cysts have been known to resolve on their own without treatment.
2. Immobilization:
In some cases, immobilizing the affected joint with a splint or brace may be recommended. This can help relieve symptoms and prevent further irritation or enlargement of the cyst.
3. Aspiration:
Aspiration is a process in which the fluid from the cyst is drained using a needle and syringe. This procedure is typically performed in a healthcare provider’s office. After numbing the area with a local anesthetic, the doctor will insert a needle into the cyst and draw out the fluid. In some cases, a corticosteroid may be injected into the cyst after aspiration to reduce inflammation and the chance of recurrence. Aspiration is a less invasive option but may have a higher risk of cyst recurrence compared to surgical removal.
4. Surgical Removal:
If the ganglion cyst is causing significant pain or functional limitations, or if it returns after aspiration, surgical removal may be considered. The procedure, known as excision, involves removing the cyst and, if necessary, a portion of the joint capsule or tendon sheath from which it originates. Surgery can be performed through open surgery or arthroscopy (using a tiny camera and specialized instruments inserted through small incisions). Surgical removal generally has a lower risk of recurrence compared to aspiration.
Speaking of surgical removal, our contributor Dr. Allen Conrad, Doctor of Chiropractic at Montgomery County Chiropractic Center, states, “Removing any type of cyst can have some complications. These may include infection, as well as scar tissue from the surgery. Discuss treatment options with your surgeon to make sure they answer any questions about removing a cyst. The concerned doctor can explain the risks and benefits and then you can make an informed decision about what can be the best step for you.”
You must understand that ganglion cysts may recur after treatment, regardless of the method used. Recovery time and outcomes can vary depending on the size and location of the cyst, as well as individual factors. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate ganglion cyst treatments based on your specific situation.
Causes And Risk Factors for Ganglion Cysts

The exact causes of ganglion cysts are not fully understood. However, several factors may contribute to their development. Here are some common causes and risk factors associated with ganglion cysts:
1. Tendon or Joint Irritation:
Ganglion cysts often develop near joints or tendons that have experienced repetitive stress or trauma. Activities that involve repetitive motions or joint overuse, such as typing, playing certain musical instruments, or sports activities, may increase the risk of developing a ganglion cyst.
2. Joint or Tendon Injury:
A previous injury to a joint or tendon, such as a sprain or strain, can trigger the formation of a ganglion cyst. It is believed that the injury causes the joint lining or tendon sheath to weaken or tear, leading to the leakage of synovial fluid and the subsequent formation of a cyst.
3. Synovial Joint or Tendon Sheath Abnormalities:
Abnormalities in the synovial joints or tendon sheaths may contribute to the development of ganglion cysts. These abnormalities can create areas of weakness or vulnerability where the synovial fluid can accumulate and form a cyst.
4. Age and Gender:
Ganglion cysts are more common in women, particularly those between the ages of 20 and 40. The exact reasons for this gender and age predilection are not fully understood.
5. Genetic Predisposition:
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing ganglion cysts. Certain genetic factors may influence the strength and integrity of joint linings or tendon sheaths, making them more prone to cyst formation.
6. Osteoarthritis and Joint Degeneration:
Ganglion cysts have been associated with joint degeneration and osteoarthritis. The breakdown of cartilage and other joint tissues in these conditions may contribute to the formation of cysts.
It is important to note that while these factors may increase the likelihood of developing ganglion cysts, they do not guarantee their occurrence. Ganglion cysts can still develop without any apparent cause or risk factors.
Prevention Tips
While there is no foolproof way to prevent ganglion cysts, there are certain measures you can take that may help reduce the risk or minimize their occurrence. Here are some prevention tips:
Avoid Repetitive Joint or Tendon Stress:
Engage in activities that promote joint health and avoid excessive repetitive stress on your joints and tendons. Don't even think of popping ganglion cyst on your own — it can get infected. If you have a job or hobby that involves repetitive motions, take regular breaks, vary your tasks, and practice proper ergonomics to reduce the strain on your joints.
Protect Your Joints:
Use protective gear or equipment when participating in activities that pose a risk of joint injuries, such as sports or manual labor. Wearing supportive braces or wraps can help stabilize and protect your joints.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Excess weight can place additional stress on your joints, increasing the risk of joint problems and potentially ganglion cysts. Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise to reduce the strain on your joints.
Warm-up and Stretch:
Prior to engaging in physical activities or sports, warm up your muscles and joints with gentle exercises. Incorporate stretching exercises to improve joint flexibility and reduce the risk of injury.
Practice Joint-Friendly Techniques:
When performing repetitive tasks or using tools, adopt proper body mechanics and techniques to minimize joint strain. Use ergonomic tools and workstations that support good joint posture and reduce the risk of repetitive stress injuries.
Take Breaks and Rest:
If you perform activities that involve repetitive motions, take regular breaks to rest your joints and avoid overuse. Listen to your body and give yourself adequate time to recover after intense physical activities.
Pay Attention to Joint Health:
Maintain good overall joint health through a balanced diet rich in nutrients that support joint function. Regular exercise, including strength training and low-impact activities like swimming or cycling, can help keep your joints strong and flexible.
Ganglion cysts, though often harmless, can present challenges in terms of discomfort, mobility, and aesthetics. However, through medical intervention and informed decision-making, individuals can find relief and restore their quality of life.
It is important to remember that each case of ganglion cyst is unique, and consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment. Whether it involves observation, immobilization, aspiration, or surgical removal, the journey toward resolution requires expert guidance and individualized care.
Contributor: Dr. Allen Conrad, BS, DC, CSCS, and Owner of Montgomery County Chiropractic Center





 JOIN OUR WHATSAPP CHANNEL
JOIN OUR WHATSAPP CHANNEL

























































